Trial Period or Updates Expiring? Email Trial ID to Support
Thank you for testing MillMage!
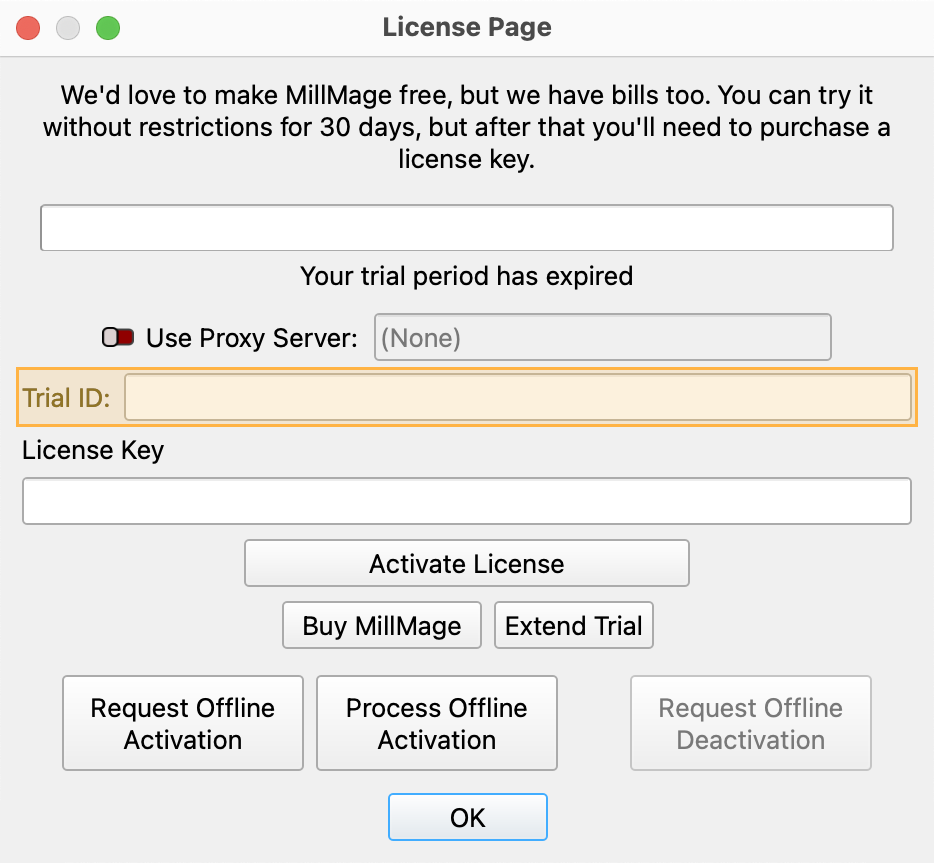
Release Candidate users who see a "Your trial period has expired" notice when opening MillMage can request an extension to the update period by emailing the MillMage Trial ID to the Support team.
Find your Trial ID in the License Management window. Email your Trial ID to [email protected] to start your request. The duration of the extended update period may vary.
Warning
The current version of MillMage is a Release Candidate — a stable version of software that is nearly ready for official release, but in need of additional public testing. Please report any unexpected behavior in the MillMage Software Questions section of our forum, including screenshots and as much detail as possible. Ask hardware compatibility questions in the MillMage Hardware Compatibility section.
Users new to MillMage should follow the Getting Started guide.
Video: How to Use a Release Candidate
This video features our sister software, LightBurn. While there may be slight differences in appearance and layout, the demonstrated processes are similar in MillMage.
Warning
This documentation is in active development and in a prerelease state. These documents are not complete and may include missing pages, broken links, and placeholders. Content is being updated as feedback is reviewed. Your patience is appreciated.
Dogbone Slot
Dogbone Slots are a special type of Pocket operation that carves extra space at the corners of assigned shapes.
The extra space allows the slot to accommodate inserted pieces with sharp corners that would not otherwise fit if the slot had the arced corners characteristic of a standard Pocket operation.
Selecting the correct style of slot can conceal or minimize the amount of the slot that is visible when the pieces are joined together.
Assigning shapes to a Dogbone Slot operation leaves the original geometry in your Workspace unchanged — you'll only see the difference when you Preview or Start a job.
Note
Only rectangular shapes are valid for use with Dogbone Slot operations. The longer side of the rectangle must exceed the shorter side in length by at least 1 mm.
-

Both of these rectangles are identical. The top is assigned to a Dogbone Slot operation, while the bottom is assigned to a Pocket operation. -

Although the geometry of the shapes in the Workspace remains unchanged, MillMage will tell your router to carve a slightly altered area, expanding the corners. -

The outline of a standard Pocket is represented in black, and a rectangular insert is represented in red. Notice how the corners of the red insert are outside the arcs at the Pocket's corners — it won't fit. -

With the extra carved areas applied by the Dogbone Slot, there is now enough space to accommodate the corners of the rectangular insert — it will fit.
Dogbone Slot Mode Settings¶
Click any option in the image below to jump directly to the relevant section for that option, or scroll down for a list of options and descriptions.
Sections that have special settings for Dogbone operations are listed just below, while common settings that apply similarly to most or all other types of operations are listed toward the bottom.
Note
For information on options that are unique to other types of operations, see Other Operations, below.
Clearing Pattern¶
Cut Direction¶
Controls the direction your router will move while carving.
-
Conventional milling moves the router against the rotation of the spindle.
-
Climb milling moves the router in the same direction as the spindle rotates.
Cut Preview¶
The Cut Preview depicts the movement of the router and rotation of the spindle relative to the material, as determined by your current Cut Direction selection.
Style¶
You can select from three Styles of Dogbone Slots — each will affect the resulting carving slightly differently.
- Inline carves extra space at the corners, on the short sides of an assigned rectangle.
- Side carves extra space at the corners, on the long sides of an assigned rectangle.
- Minimal carves extra space centered on the point of each corner of the original rectangle.
Pattern Preview¶
Depths and Steps¶
Equation Support and Automatic Unit Conversion
The Depths and Entry/Steps fields in the Operation Settings Editor support equations and automatic unit conversion.
For example:
-
To cut to a final depth of ¼ in, type
1/4in the Diameter field, then click in another field, and MillMage will convert to the value to0.75.Addition (
+), subtraction (-), and multiplication (*), are all also supported. -
If your display units are set to metric but you've taken measurements in imperial, you can enter
1/4 inand MillMage will convert the value to6.350 mm. This works in reverse as well, converting metric units to imperialMultiple notations are supported, including
ft,',", andmm.
Start Depth¶
The depth, relative to the surface of your stock, at which the operation will begin carving or cutting.
A value of 0 means it will begin at the top of your material — any value greater than 0 will tell your router to begin carving below the surface of the material.
Final Depth¶
The depth, relative to the surface of your stock, at which the operation will stop carving or cutting.
Final Depth is the total depth of the material that will be removed from your stock.
Depth Per Pass¶
Specifies the depth of material to be cleared with each pass of your router. The total number of passes is equal to Final Depth / Depths Per Pass.
For example, if you set Depth Per Pass to 1 mm, and Final Depth to 10 mm, your router will make 10 passes of 1 mm each.
Step Over¶
Step Over controls the distance between each path of your chosen clearing pattern. A larger Step Over leads to greater distance between each path.
Step Over (%)¶
Enter a percentage in the Step Over (%) field to apply a Step Over value as a percentage of your tool's diameter.
In other words, if your tool's diameter is 0.125", entering 50% in the Step Over (%) will set the Step Over value to 0.0625".
These values are linked in both directions — if you adjust the absolute value in the Step Over field, the value in the percentage field will change to indicate the Step Over value's percentage of your tool's diameter.
Common Settings¶
Click here for information on settings that apply similarly to all types of operations
Name¶
Use this field to edit the display name of the operation in the Operations Window. By default, all operations will be named according to their type.
Paint Color¶
Click the Paint Color button to open the Select Color window, which controls the color by which the operation will be indicated in the Preview window, if Show paint colors is enabled.
You can choose from a number of Basic Colors presented at the top left of the window, or create a custom color.
To create a custom color:
-
Press Pick Screen Color to hover your cursor over any color on your screen. Click to select the color you're hovering over.
-
Use the color gradient and shading slider at the top right.
-
Adjust numeric or hexidecimal values at the bottom right to create a custom color.
-
After creating a custom color, click Add to Custom Colors to save it for future use.
Click OK to apply the color to your operation, or Cancel to exit the window thout applying the color.
Output¶
Controls whether the operation will be sent to your CNC when you Preview your project, press the Start button in the Job Control Window, or save your project in GCode format.
Auto Use Layer¶
Enable this switch to automatically apply this operation to all shapes set to a given layer. Designate the layer by clicking the button to the right of the switch.
Note
When Auto Use Layer is enabled, you can still Assign Operations to graphics set to any other layer, as normal, but all graphics assigned to the chosen layer will also have the Operation applied to them.
Tool Setup¶
Select Tool¶
Press the Select Tool button to open your Tool Library and select a tool to assign to the operation.
MillMage will automatically filter for appropriate tools for the type of operation you've selected. Some operations require specific tool geometries — if a tool's geometry is not appropriate for the type of operation you've selected, it will be unlisted and not selectable.
Tool Information¶
The remaining fields in this section display information about your selected tool, as entered in the Tool Library.
Tool Name¶
The name you gave the chosen tool in the Tool Library.
Diameter¶
The diameter of the cutting edge of your tool.
Cut Length¶
The length of the cutting edge of the chosen tool, from the top to the bottom of all flutes.
# of Flutes¶
The number of flutes on the chosen tool.
Feeds and Speeds¶
The Feeds and Speeds saved to a given tool from your Tool Library are automatically entered in the Operation Settings Editor when you select that tool.
To enter speeds in units other than what's set in Device Settings, enter the measurement including in/" or mm to specify the units you want. MillMage will automatically convert to the appropriate units as shown in the example below.
What Feeds and Speeds should I use?
The proper Feed and Speed settings depend on your tool, machine, material, and use case. In short: there's no easy answer to that question.
For specific recommendations, the best resource is usually the manufacturer of your machine or tool.
Feed Rate¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move laterally (along the X and Y axes) during operations.
Ramp Rate¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move vertically (along the Z Axis) during ramp movements.
Spindle Speed¶
Controls the speed at which your router will rotate your tool.
Note
Not all CNCs allow Spindle Speed control through software. Some have routers which must be adjusted manually.
Plunge¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move vertically (along the Z Axis) during plunge movements.
Chip Load¶
The Chip Load calculation shows the thickness of material removed by each cutting edge of a tool, during a single revolution of the spindle.
Chip Load = Feed Rate / (Spindle Speed (RPM) x # of Flutes)
The optimal Chip Load varies according to your tool and material. For specific recommendations, the best resource is usually the manufacturer of your machine or tool.
Excessively low Chip Loads produce dust, wear out bits more quickly, and risk overheating the tool and burning the edges of cuts. Excessively high Chip Loads produce chips that clear inefficiently, and may overstress and break the bit.
Vacuum and Coolant¶
Enable Vacuum¶
Enable this setting to automatically turn on your vacuum system when this operation begins.
This option requires a vacuum system that is connected to your CNC's controller.
Enable Coolant¶
Enable this setting to automatically turn on your coolant system when this operation begins.
This option requires a coolant system that is connected to your CNC's controller.
Other Operations¶
All types of operations are listed below. Select an operation to learn more about the settings available for that type of operation.
For more help using MillMage, please visit our forum to talk with MillMage staff and users, or email support.










