Trial Period or Updates Expiring? Email Trial ID to Support
Thank you for testing MillMage!
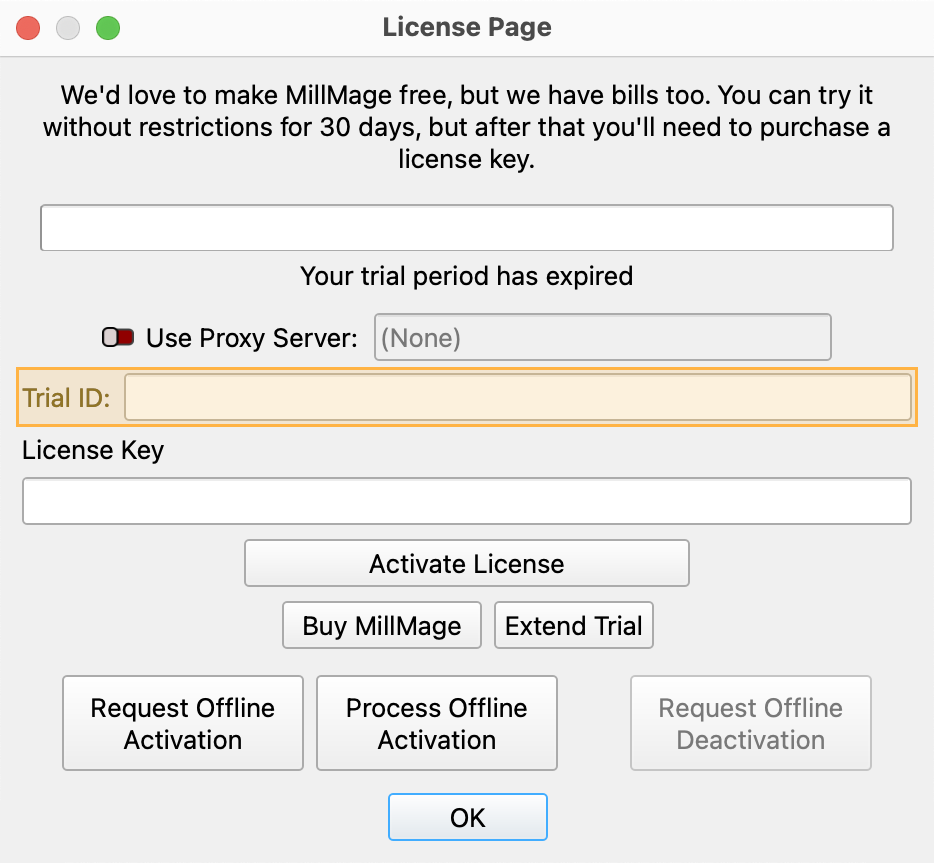
Release Candidate users who see a "Your trial period has expired" notice when opening MillMage can request an extension to the update period by emailing the MillMage Trial ID to the Support team.
Find your Trial ID in the License Management window. Email your Trial ID to [email protected] to start your request. The duration of the extended update period may vary.
Warning
The current version of MillMage is a Release Candidate — a stable version of software that is nearly ready for official release, but in need of additional public testing. Please report any unexpected behavior in the MillMage Software Questions section of our forum, including screenshots and as much detail as possible. Ask hardware compatibility questions in the MillMage Hardware Compatibility section.
Users new to MillMage should follow the Getting Started guide.
Video: How to Use a Release Candidate
This video features our sister software, LightBurn. While there may be slight differences in appearance and layout, the demonstrated processes are similar in MillMage.
Warning
This documentation is in active development and in a prerelease state. These documents are not complete and may include missing pages, broken links, and placeholders. Content is being updated as feedback is reviewed. Your patience is appreciated.
Configure GRBL Devices
Most GCode-based CNC machines are compatible with MillMage, but if you have a less common machine, you might need to make some simple changes to get the most from MillMage.
Quick Reference¶
- You might need to adjust your spindle max RPM value (
$30) to match the MillMage default (1000) or vice versa. The value in MillMage is called S-Value Max in Device Settings. - Using a laser on your CNC machine? You might need to enable Laser Mode if you have GRBL 1.1f or later (
$32=1) - If you have an older version of GRBL (prior to 1.1f) upgrading the firmware is highly recommended, as Laser Mode also prevents the machine from pausing with every power change. The pause, which happens on older versions, or when not using Laser Mode, will cause excessive burn spots when engraving images.
- Make sure the controller is reporting positions in mm, as expected by MillMage (
$13=0) - If your machine does not have homing switches (also called limit switches) you will need to home it manually.
GRBL Flavors for Lasers¶
GRBL firmware was originally designed for CNC machines and 3D printers, with laser support added more recently. It is highly configurable, and this is both a blessing and a curse. The "standard" way a CNC machine is configured is somewhat different from the way laser machines often are. Luckily this is easy to change, and easy to switch from one to the other.
More recent versions of GRBL (1.1f and up) support two laser-oriented features. The first is Laser Mode, enabled by setting $32=1 in the firmware settings. Laser mode eliminates the pauses that happen when changing power output, because GRBL knows it's controlling a laser which reacts instantly, instead of waiting for a spindle to change RPM.
The second is a feature called variable power mode, or the M4 command. In this mode, GRBL adjusts the laser power as the machine speeds up and slows down, making for very consistent cutting and marking. Older versions of GRBL do not have this feature, and simply run the laser at a constant power output for the duration of a cut. Since the machine needs to slow down to take sharp corners, this means corners get over-burnt, while long straight lines end up lighter. This also has the benefit that when the laser comes to a complete stop, the beam turns off (zero speed equals zero power), meaning that pausing a job automatically turns off the laser. This is not always true with other versions of GRBL.
If you aren't already running GRBL 1.1f (or later) on your controller, we highly recommend it for laser use. If this isn't an option, that's ok, but your results won't be as good, and pausing the laser runs the risk of leaving the beam on and ruining the job.
Getting Machine Settings¶
Many GRBL based machines allow the settings of the machine to be easily exported or viewed. For advanced configuration like adding limit switches, updating firmware, or setting up a new controller, you'll need to interact with these values. You can do this in MillMage by using the Console window or the Machine Settings window to copy, update, or reset your machine settings.
The Machine Settings window provides you with a formatted table with the parameters labeled. You can also export these settings to a file for later restoration.
In the Console Window, enter $$ to have the controller return the machine's configuration. This will show the settings in plain text, requiring more familiarity with what each command means but allowing you to view the configuration directly, without any chance of mislabeling based on custom vendor configurations.
Other Machines¶
If you aren't sure how to configure your machine, the following steps will help you figure it out.
Figure out which firmware you're running
In MillMage, when you first connect to the machine the console will typically show a "hello" message from the controller. For Smoothieware boards it is just Smoothie. For GRBL, it will be GRBL 1.1f [$ for help] or similar - this tells you it's GRBL, and which version. Machines using GRBL 1.1f or later will support the M4 variable power command, and just use the "GRBL" driver in MillMage. GRBL 1.1e or older (GRBL 1.0, GRBL 0.9, etc.) must use the GRBL-M3 device in MillMage.
Find the machine origin and coordinate direction
- Home the machine by pressing the Home button in the Move window.
- In the console window, type
G0 X0 Y0and press Enter. This will command your machine to head toward its origin position - the location represented by (0, 0) in the machine's coordinate system. This is not always the same as the home position. The origin is usually either the front left corner or the rear right corner of the machine, but can be a different corner or the center of the work area. If your machine moved to the center, skip to Center Origin Machines for more information. - After the machine has stopped moving from the previous command, type
G0 X10 Y10and press Enter. If your machine moves 10 mm into the work area on both axes, your machine uses positive workspace coordinates. You can set the origin in MillMage to match the machine origin you found in step 2. If your machine bumped the rails, it uses negative coordinates.
Machines without homing sensors or limit switches¶
If your machine does not have homing switches (also called limit switches) you will need to home it manually. There are two ways to do this:
- With the machine off, manually move the tool to the origin position (usually front-left), then power up the machine. Until you tell it otherwise, the power-on location of the controller is treated as the zero position.
- With the machine powered, jog the tool to the origin position. In the console window, type:
G92 X0 Y0and press Enter. TheG92command tells GRBL to set the current location as the specified coordinate, so you're telling the machine "this is zero". You will also need to set$10=0for this to work correctly.
If you use the second option frequently, you may want to save the command as a macro.
For more help using MillMage, please visit our forum to talk with MillMage staff and users, or email support.

