Trial Period or Updates Expiring? Email Trial ID to Support
Thank you for testing MillMage!
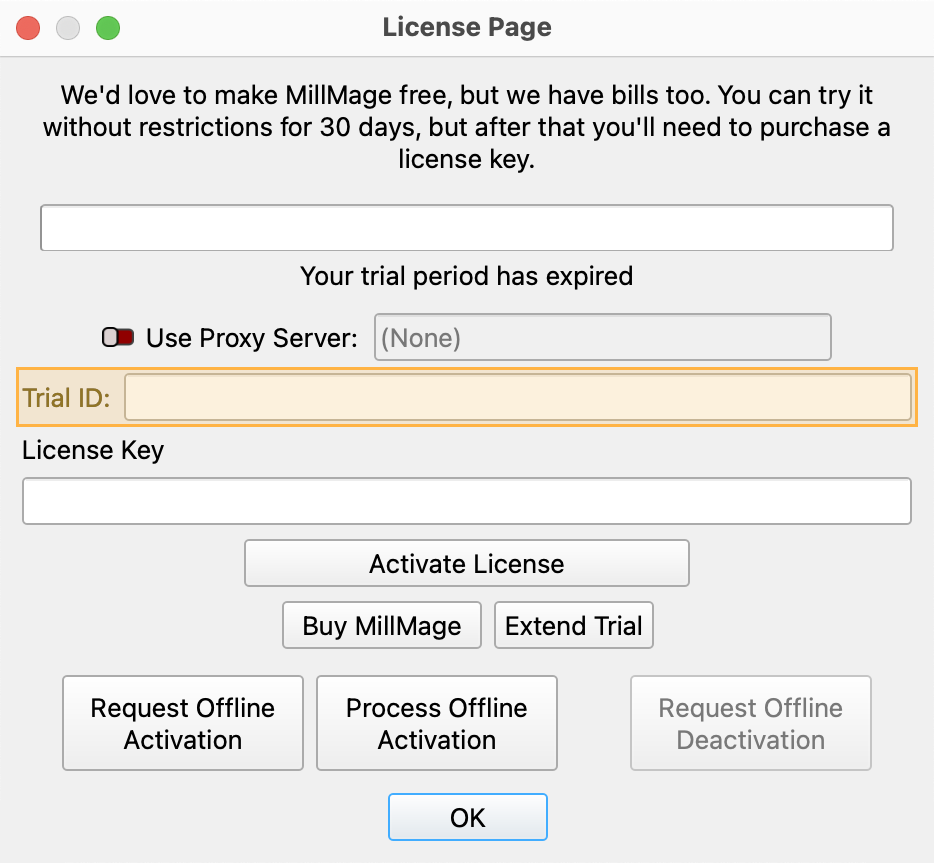
Release Candidate users who see a "Your trial period has expired" notice when opening MillMage can request an extension to the update period by emailing the MillMage Trial ID to the Support team.
Find your Trial ID in the License Management window. Email your Trial ID to [email protected] to start your request. The duration of the extended update period may vary.
Warning
The current version of MillMage is a Release Candidate — a stable version of software that is nearly ready for official release, but in need of additional public testing. Please report any unexpected behavior in the MillMage Software Questions section of our forum, including screenshots and as much detail as possible. Ask hardware compatibility questions in the MillMage Hardware Compatibility section.
Users new to MillMage should follow the Getting Started guide.
Video: How to Use a Release Candidate
This video features our sister software, LightBurn. While there may be slight differences in appearance and layout, the demonstrated processes are similar in MillMage.
Warning
This documentation is in active development and in a prerelease state. These documents are not complete and may include missing pages, broken links, and placeholders. Content is being updated as feedback is reviewed. Your patience is appreciated.
Tool Library
The Tool Library is where you create and save entries containing information on the tools you'll use with your CNC.
When you create and edit operations, you'll be able to Select a saved tool from your library, and MillMage will use the stored information for the chosen tool when calculating the toolpaths it sends to your CNC.
In order to create any operation, you'll need to have at least one tool in your Tool Library.
Info
For a step-by-step guide on creating your first Tool Library, see Get Started: Tool Library.
Tool Library Management¶
Several options in the Tool Library window allow you to create and manage categories of tools, and tools within them.
Click any option in the image below to jump directly to the relevant section for that option, or scroll down for a list of options and descriptions.
Note
To confirm any change in the Tool Library window, you must press OK to save and exit. Closing the window or clicking Cancel will discard any changes you've made.
Tool List¶
All of your categories and tools are displayed on the left side of the Tool Library window.
Click any category to select it, enabling the Create New Tool in Selected Category, Edit Category, Copy Category, and Delete Category options for that category. Click the arrow to the left of a category to expand it, showing the tools contained within.
Click any tool to display information on the right side of the window, and to enable the Edit Tool, Copy Tool, and Delete Tool options for that Tool.
New Library¶
Creates a new Tool Library.
Your system's file browser will open, where you can name your new library and choose a location on your computer to save it to. The library will be saved with the .tools file extension.
Each library contains a unique list of categories and tools, and you may only have one library loaded at one time.
File Path¶
The save location of your Tool Library on your computer is shown above the Tool List.
Load Library¶
Opens your system's file browser, where you can navigate to the location of a pre-existing Tool Library saved with the .tools file extension.
Create New Tool in Selected Category¶
After clicking to select a category from the list, click this button to create a new tool within that Category.
You will immediately have access to edit the fields in the Tool Properties section of the Tool Library window, for the new tool. See below for information on these fields.
Note
You must create at least one category before creating a tool.
Create New Category¶
Creates a new category within your Tool Library.
After clicking, you will see <New Category> appear in the list. Type to give the category a new name, then press enter or click anywhere else in the list to confirm the name.
Tip
How you choose to organize your tools is up to you — you can organize by Tool Geometry, material type, or even machine, if you've got multiple CNCs in your shop.
Edit Tool or Category¶
Click this button to edit the currently selected tool or category in the list. You can also double-click a category or tool to edit its name or properties.
-
For categories, this will allow you to edit the name by typing, then pressing enter or clicking anywhere else in the list to confirm the new name.
-
For tools, this will allow you to edit each of the fields in the Tool Properties section.
Note
You must click Apply Changes to confirm any edits you've made to the Tool's properties. Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Copy Tool or Category¶
Click this button to duplicate the currently selected tool or category in the list.
If you copy a tool, you'll immediately be able to edit each of the fields in the Tool Properties section.
Note
You must click Apply Changes to confirm the creation of the duplicate, along with any edits you've made to its properties. Click Cancel to discard the duplicate.
Delete Tool or Category¶
Click this button to delete the selected tool or category.
Note
The deletion of a tool or category will not be permanently saved until you click OK to close out of the Tool Library window. If you inadvertently delete a tool or category you wish to keep, press Cancel to close out of the Tool Library and discard the change.
Tool Properties¶
The Tool Properties section of the Tool Library window displays details of the currently selected tool, along with a depiction of the tool's geometry.
When you select Create New Tool in Selected Category, Edit Tool, or Copy Tool, you'll have access to adjust these settings.
Note
You must click Apply Changes to confirm any edits you've made to the Tool's properties. Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Click any parameter in the adjacent image to jump directly to the relevant section for that option, or scroll down for a list of parameters and descriptions.
Some options specific to tool Geometries other than End Mill are not shown in the image, but are listed below.
Geometry Dropdown Menu¶
Use the dropdown menu to select from five different types of Tool Geometry. Your selection affects the types of Operations you will be able to Select to use a given tool for, and the appearance of the simulation in the Preview window.
-
End Mills have sharp edges that cut material as the tool rotates and moves laterally (along the X and Y axes).
The bottom of a standard End Mill is flat with sharp corners, resulting in flat clearings, and 90-degree corners at the edges of cleared areas.
Some End Mills have rounded corners meeting at a flat surface, and produce flat clearings, but sloped corners at the edges of cleared areas. You can enter the radius of the rounded corner in the Corner Radius field of the Tool Properties section.
-
Ball Mills have completely rounded tips, resulting in rounded grooves with sloped edges where the tool has carved. Ball Mills are typically not used for clearing large areas.
-
V-Bits have angled tips that can create Chamfered edges, or angled grooves in material.
-
Drill bits have sharp tips to make vertical cuts (along the Z axis) into material.
-
Round-over bits have an inverted radius meeting at a tip, used to created rounded edges rather than sharp corners.
-
Scribe bits are used to precisely engrave a design by dragging its diamond coated tip over the surface of the material. Set the Spindle Speed to zero RPM as scribes do not need to rotate to function.
Geometry Depiction¶
On the right side of the Tool Library window you'll see a depiction of your tool's appearance, given the parameters you've entered. As you make adjustments to the Tool Properties, the appearance will live-update.
Name¶
The display Name for your tool. Note that the Name you enter will always display after the Tool's Geometry and Diameter.
For example, an End Mill with a ⅛ inch diameter named Upcut, will display as:
End Mill, 1/8 in : Upcut
Vendor¶
The name of the manufacturer that created or supplied this tool. This field is optional and for organizational purposes only.
Tool Number¶
Used on CNCs with automatic tool changers. MillMage will use this number to tell your machine to change to the correspondingly numbered tool before beginning an operation.
Note
You must enable Output Tool Change and Has Automatic Tool Changer in the Custom GCode tab of the Device Settings window for MillMage to use this feature.
Diameter¶
Equation Support and Automatic Unit Conversion
The fields in the Tool Properties section support equations and automatic unit conversion.
For example:
-
If your tool's diameter is ¼ inch, type
1/4in the Diameter field, then press enter, and MillMage will convert to the value to0.75.Addition (
+), subtraction (-), and multiplication (*), are all also supported. -
If your display units are set to metric but your tool supplier provides measurements in imperial, you can enter
1/4 inand MillMage will convert the value to6.350 mm.Multiple notations are supported, including
ft,',", andmm.
The diameter measured across the cutting edge of your tool.
Flute Length¶
The length of the cutting span of the chosen tool, from the top to the bottom of all flutes. Also known as the cut length.
Note
For V-Bits and Scribes, this value is automatically calculated and cannot be manually adjusted.
# of Flutes¶
The number of flutes on the tool. Flutes are channels cut into the tool shaft that evacuate material chips from the workpiece.
Corner Radius¶
End Mills, V-Bits, Scribes and Round-over Bits Only
This option is adjustable only when the Geometry of the selected tool is set to End Mill, V-Bit, or Round-over.
This value defines the radius of arcs on both sides of the tip of the tool. For End Mills the arc is convex and for Round-over bits it is concave.
Tip Radius¶
V-Bits Only
This option is adjustable only when the Geometry of the selected tool is set to V-Bit or Scribe.
This value defines the radius for V-Bits with rounded tips. Set to the zero if the V-Bit has a sharp tip or is a scribe.
Included Angle¶
V-Bits, Drills, and Scribes Only
This option is adjustable only when the Geometry of the selected tool is set to V-Bit, Drill, or Scribe.
The angle of the cutting edge as measured from the tool shank to the centerline.
Tip Length¶
Round-over Tools Only
This option is adjustable only when the Geometry of the selected tool is set to Round-over.
The length of the cutting tip at the bottom of the tool.
Display Units¶
The units of distance and speed that will display alongside the tool. Select Automatic to use your default MillMage settings, or Metric to display metric units.
Feeds and Speeds¶
The Feeds and Speeds saved to a given tool in your Tool Library are automatically entered in the Operation Settings Editor when you select that tool. You may make manual adjustments to these settings after a tool has been applied to an operation.
What Feeds and Speeds should I use?
The proper Feed and Speed settings depend on your tool, machine, material, and use case. In short: there's no easy answer that question.
For specific recommendations, the best resource is usually the manufacturer of your machine or tool.
Feed Rate¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move laterally (along the X and Y axes) during operations.
Plunge Rate¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move along the Z Axis during plunge movements.
Ramp Rate¶
Controls the speed at which your CNC will move along the Z Axis during ramp movements.
Spindle Speed (RPM)¶
Controls the speed at which your router will rotate your tool.
Note
Not all CNCs allow Spindle Speed control through software. Some have routers which must be adjusted manually.
Chip Load¶
The Chip Load calculation shows the thickness of material removed by each cutting edge of a tool, during a single revolution of the spindle.
Chip Load = Feed Rate / (Spindle Speed (RPM) x # of Flutes)
This computation is a helpful way to understand the relationship between Feed Rate and Spindle Speed, and the resulting load placed on your router.
- Increasing the Feed Rate will increase Chip Load, when Spindle Speed is held constant.
- Increasing Spindle Speed will decrease Chip Load, when the Feed rate is held constant.
The optimal Chip Load varies according to your tool and material. For specific recommendations, the best resource is usually the manufacturer of your machine or tool.
Excessively low Chip Loads produce dust, wear out bits more quickly, and risk overheating the tool and burning the edges of cuts. Excessively high Chip Loads produce overly large chips that clear inefficiently, and may overstress and break the bit.
Scribe Bits Only
The Chip Load value will change to Drag when the tool Geometry is set to Scribe and the RPM value is set to zero.
Spindle Advance¶
Drill Bits Only
This calculation is presented only when the Geometry of the selected tool is set to Drill.
The Spindle Advance calculation shows the distance the spindle will move downward in the time it takes the tool to make on complete revolution, as determined by your Plunge Rate and Spindle Speed settings.
Spindle Advance = Plunge Rate / Spindle Speed
Depth Per Pass¶
Specifies the depth of material to be cleared with each pass of your router.
When you Select this tool for an operation, LightBurn will use this number to calculate a total number of passes equal to Final Depth / Depths Per Pass.
For example, if you set Depth Per Pass to 1 mm, and Final Depth to 10 mm, your router will make 10 passes of 1 mm each.
Step Over¶
Step Over controls the distance between each path of your chosen clearing pattern. A larger Step Over leads to greater distance between each path.
Step Over Percentage¶
Enter a percentage in the Step Over (%) field to apply a Step Over value as a percentage of your tool's diameter.
In other words, if your tool's diameter is 0.125", entering 50% in the Step Over (%) will set the Step Over value to 0.0625".
These values are linked in both directions — if you adjust the absolute value in the Step Over field, the value in the percentage field will change to indicate the Step Over value's percentage of your tool's diameter.
Related Topics¶
For more help using MillMage, please visit our forum to talk with MillMage staff and users, or email support.


