Trial Period or Updates Expiring? Email Trial ID to Support
Thank you for testing MillMage!
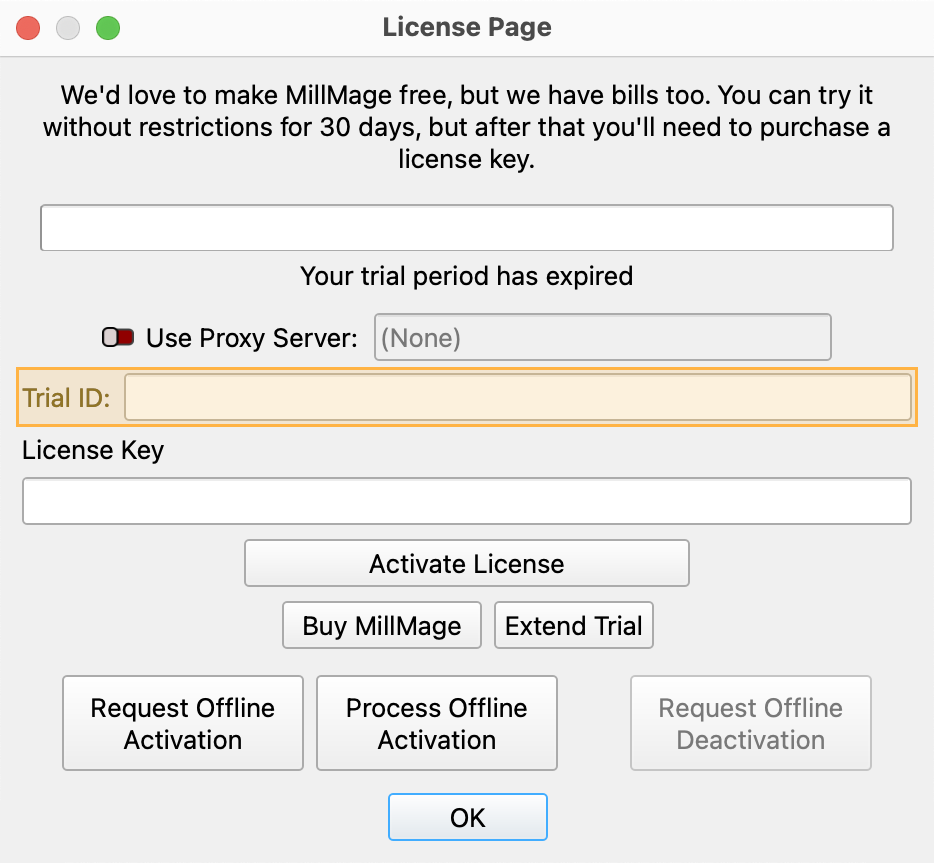
Release Candidate users who see a "Your trial period has expired" notice when opening MillMage can request an extension to the update period by emailing the MillMage Trial ID to the Support team.
Find your Trial ID in the License Management window. Email your Trial ID to [email protected] to start your request. The duration of the extended update period may vary.
Warning
The current version of MillMage is a Release Candidate — a stable version of software that is nearly ready for official release, but in need of additional public testing. Please report any unexpected behavior in the MillMage Software Questions section of our forum, including screenshots and as much detail as possible. Ask hardware compatibility questions in the MillMage Hardware Compatibility section.
Users new to MillMage should follow the Getting Started guide.
Video: How to Use a Release Candidate
This video features our sister software, LightBurn. While there may be slight differences in appearance and layout, the demonstrated processes are similar in MillMage.
Warning
This documentation is in active development and in a prerelease state. These documents are not complete and may include missing pages, broken links, and placeholders. Content is being updated as feedback is reviewed. Your patience is appreciated.
Variable Text Formatting
Use the following formatting expressions with the appropriate Variable Text mode to have MillMage replace the expressions with alternate data when you output a project to your CNC machnine.
In order for each type of formatting expression to be replaced with alternate data, you must also select the corresponding mode from the dropdown menu in the Text Options Toolbar.
Tip
Use the Test button to verify that you have entered the formatting expressions correctly, before sending a project to your CNC.
Date/Time¶
When using Date/Time formatting, MillMage will automatically substitute special combinations of characters with values for the current local date and time, as determined by your system's clock.
Use the following expressions for dates:
| Output | Expression |
|---|---|
| The day as number without a leading zero (1 to 31) | d |
| The day as number with a leading zero (01 to 31) | dd |
| The abbreviated localized day name (e.g. "Mon" to "Sun"). Uses the system locale to localize the name. | ddd |
| The long localized day name (e.g. "Monday" to "Sunday"). Uses the system locale to localize the name. | dddd |
| The numeric week of the year in ISO-8061 format (e.g. 51) | w |
| The year/week of the year in ISO-8061 format (e.g. 2025/51) | W |
| The month as number without a leading zero (1-12) | M |
| The month as number with a leading zero (01-12) | MM |
| the abbreviated localized month name (e.g. "Jan" to "Dec"). Uses the system locale to localize the name. | MMM |
| the long localized month name (e.g. "January" to "December"). Uses the system locale to localize the name. | MMMM |
| the year as two digit number (00-99) | yy |
| the year as four digit number | yyyy |
Use the following expressions for time:
| Expression | Output |
|---|---|
| h | The hour without a leading zero (0 to 23 or 1 to 12 if AM/PM display) |
| hh | The hour with a leading zero (00 to 23 or 01 to 12 if AM/PM display) |
| H | The hour without a leading zero (0 to 23, even with AM/PM display) |
| HH | The hour with a leading zero (00 to 23, even with AM/PM display) |
| m | The minute without a leading zero (0 to 59) |
| mm | The minute with a leading zero (00 to 59) |
| s | The whole second without a leading zero (0 to 59) |
| ss | The whole second with a leading zero where applicable (00 to 59) |
| z | The fractional part of the second, to go after a decimal point, without trailing zeroes (0 to 999). Thus "s.z" reports the seconds to full available (millisecond) precision without trailing zeroes. |
| zzz | The fractional part of the second, to millisecond precision, including trailing zeroes where applicable (000 to 999). |
| AP or A | Use AM/PM display. A/AP will be replaced by either "AM" or "PM". |
| ap or a | Use am/pm display. a/ap will be replaced by either "am" or "pm". |
| t | The time zone (e.g. "CEST") |
Additional Notes¶
-
Any sequence of characters enclosed in single quotes will be included verbatim in the output string (stripped of the quotes), even if it contains formatting characters.
-
Two consecutive single quotes ('') are replaced by a single quote in the output.
-
All other non-formatting characters in the input string are included verbatim in the output.
Tip
Formats without separators (e.g. "ddMM") are supported but must be used with care, as the resulting strings aren't always reliably readable (e.g. if "dM" produces "212" it could mean either the 2nd of December or the 21st of February).
Serial Number¶
When using Serial Number formatting, MillMage will automatically substitute special combinations of characters with the Current serial number value.
Use the following expressions for serial numbers:
| Output | Expression |
|---|---|
| The serial number as a decimal value | d |
| The serial number as a hexadecimal value, lower case | h |
| The serial number as a hexadecimal value, upper case | H |
| Tells MillMage to pad the number with leading zeros | 0 |
The number of characters controls how many digits will output. If the Current serial number is larger than the number of digits allowed, as many digits as will fit from the end of the number will be displayed. For example, if your Current serial number is 1234, the table below shows how that number would be formatted for each of the displayed formatting inputs:
| Input | Output | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| d | 4 | 0d | 4 |
| dd | 34 | 0dd | 34 |
| ddd | 234 | 0ddd | 234 |
| dddd | 1234 | 0dddd | 1234 |
| ddddd | 1234 | 0ddddd | 01234 |
| dddddd | 1234 | 0dddddd | 001234 |
Additional Notes¶
-
Any sequence of characters enclosed in single quotes will be included verbatim in the output string (stripped of the quotes), even if it contains formatting characters.
-
All other non-formatting characters in the input string are included verbatim in the output.
-
Use the Offset field in the Text Options Toolbar to enter multiple indentical formatting strings that output a different serial number.
-
You cannot mix decimal and hexadecimal formatting in the same text entry.
-
You cannot split a serial number with other characters. For example, because of the hyphen between the two groups of format characters, this string is not valid: ddd-ddd.
-
Invalid strings will output as "bad serial format".
Merge/CSV¶
When using Merge/CSV formatting, MillMage will automatically substitute special combinations of characters with an entry from a CSV file.
A CSV file is a Comma Separated Values file — a very simple text format that uses a line in a file as the row, and commas to separate columns. You can create a CSV file using a plain text editor, or by exporting from most common spreadsheet software.
In a Merge/CSV entry in MillMage, the text you enter uses the percent sign followed by a number to look up a column in the current row of the CSV file.
-
Columns and rows are numbered starting from 0.
-
Refer to the first column in a CSV using the formatting "%0", the second using "%1", the third using "%2", and so on.
-
A Current value of 0 refers to the first row, 1 to the second, 2 to the third, and so on.
For example, using a CSV file with the following content:
And entering this formatting:
"I use %0 with my %1"
Would output:
"I use LightBurn with my laser cutter" or "I use MillMage with my CNC router"
Special Characters Displaying Incorrectly
To fix this problem, open the file in a modern text editor or spreadsheet program and save with UTF-8 encoding. Notepad on Windows and TextEdit on macOS both work well for this and come pre-installed with the operating system.
Additional Notes¶
- Use the Offset field in the Text Options Toolbar to enter multiple indentical formatting strings that output a different row from a CSV.
Additional Notes¶
-
Any sequence of characters enclosed in single quotes will be included verbatim in the output string (stripped of the quotes), even if it contains formatting characters.
-
All other non-formatting characters in the input string are included verbatim in the output.
Related Topics¶
For more help using MillMage, please visit our forum to talk with MillMage staff and users, or email support.







